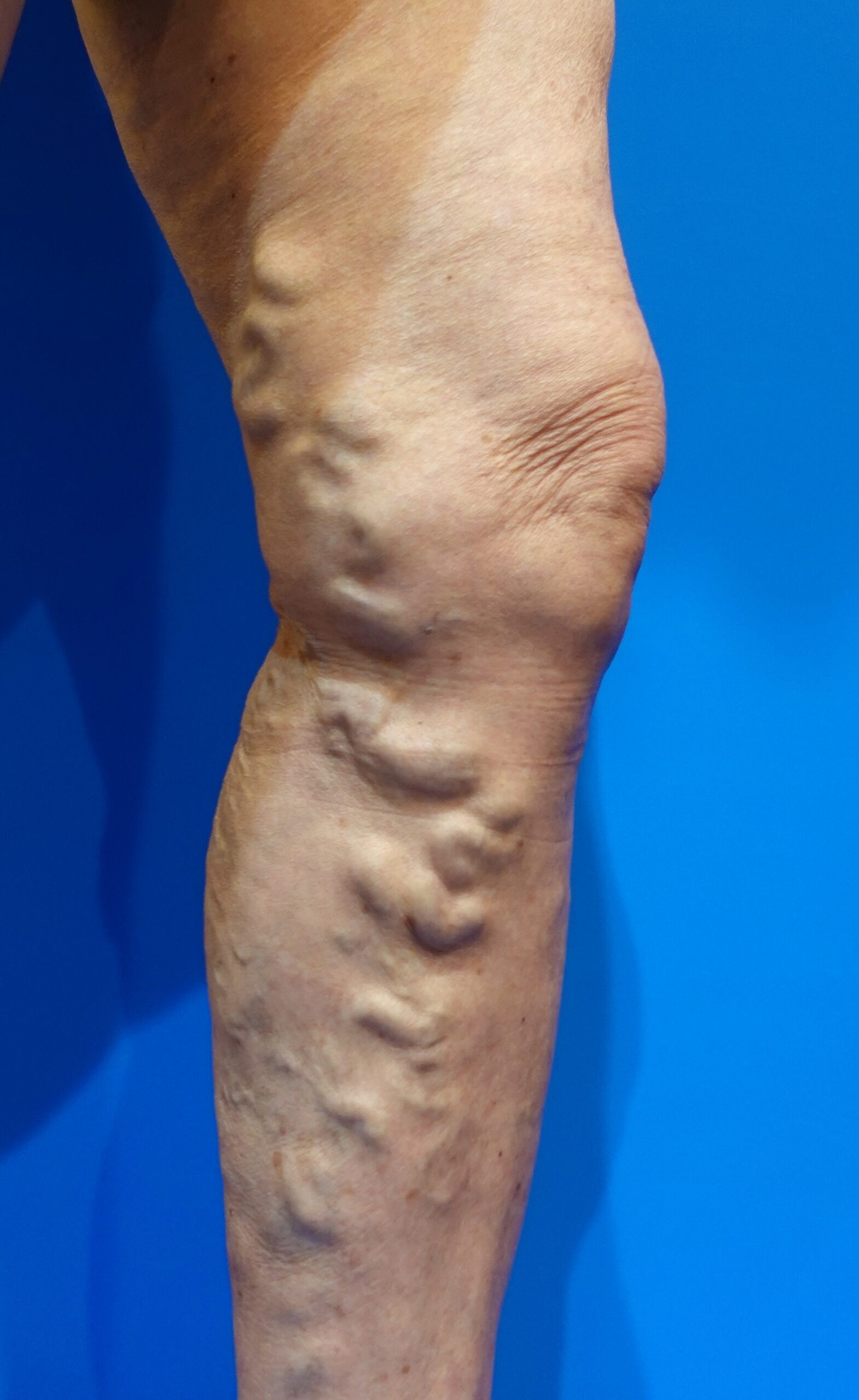
Surgical method for varicose veins
Major surgical methods for varicose veins currently performed in Japan are as follows.
・Endovenous ablation (laser catheter or radiofrequency catheter)
・Endovenous embolization (medical adhesive )
・Stripping (classic surgery)
There is a surgical method called “high ligation”, but this method has a very high recurrence rate, therefore rare vascular surgeon will perform this method.
Endovenous ablation
Among the surgical methods for varicose veins, endovenous ablation is currently the most performed in the world. Endovenous ablation is a treatment in which a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into a vein to burn it from the inside and occlude it.
There are two types of catheters.
- Laser catheter
- Radiofrequency catheter
 laser catheter
laser catheter
 radiofrequency catheter
radiofrequency catheter
What they both have in common is that they use heat to burn the veins from the inside and occlude them.
A laser catheter emits a 1470nm laser from the tip of the catheter, and the heat from this laser burns the vein from the inside. Veins are made of protein, so when heat is applied, they shrink, harden, and become obstructed. Laser catheters have a narrow laser irradiation range, so they can cauterize varicose veins over very short distances and are extremely flexible. All types of ablation are possible.
Radiofrequency catheter generate heat from a metal coil wrapped around the tip of the catheter.
It is designed to burn veins at 120 degrees Celsius using the heat emitted from the tip of the radiofrequency catheter. The coil at the tip of the radiofrequency catheters are 3.0cm and 6.5 cm long, so it is not possible to cauterize veins shorter than 3.0 cm. Also, it is not possible to cauterize twisted and tortuous veins.
Laser catheters are superior in that they can be used flexibly to treat any type of varicose veins.
Endovenous embolization
The latest surgical method for varicose veins is endovenous embolization. Also called ”glue treatment”.Endovenous ablation “burns” the veins to block them and prevent blood from flowing backwards. In contrast, endovenous embolization involves “gluing” the vein with an adhesive to occlude it and prevent blood from flowing backwards. This treatment uses an adhesive called “cyanoacrylate”. Fill the syringe with cyanoacrylate and place it into the pistol-shaped syringe. A long, thin catheter is inserted into the vein and cyanoacrylate is injected to glue and occlude the vein. The procedure is exactly the same as the glue gun used for DIY.
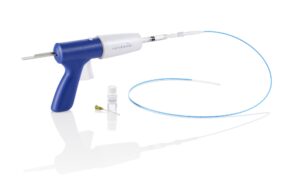
Difference between endovenous ablation and endovenous embolization
Endovenous embolization obstructs the vein by “burning” it, so if the area around the vein is not anesthetized, the patient will scream, “It’s hot!” In contrast, endoveonous embolization occludes the vein by “gluing” it, so there is no need to anesthetize the area around the vein. Therefore, the advantage is that there is almost no pain after surgery. However, in reality, the pain after endovenous ablation is not severe. Most patients go without taking painkillers.
Stripping
Stripping has been the gold standard for varicose vein surgery for almost 100 years. The vein is pulled out using a wire called a “stripper”. For a long time, this was the standard surgical method for varicose vein surgery, but also have three problems.
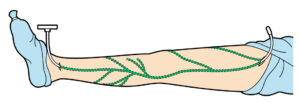
1. Requires skin incision
2. Internal bleeding
3. Strong pain after surgery
These disadvantages of stripping have been improved with the advent of endovenous ablation and endovenous embolization. Nowadays, this technique has become an endangered species. It’s safe to say that the era of stripping is almost over. However, medicine is constantly advancing.
Isn’t it best for patients to have a treatment that is painless and cures properly?
Summary
We explained the surgical method for varicose veins. Each methods have its advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to consider the characteristics of each and the condition of the patient’s varicose veins when selecting a surgical method.