Detailed Explanation of Vulvar Varicose Veins
What are Vulvar Varicose Veins?
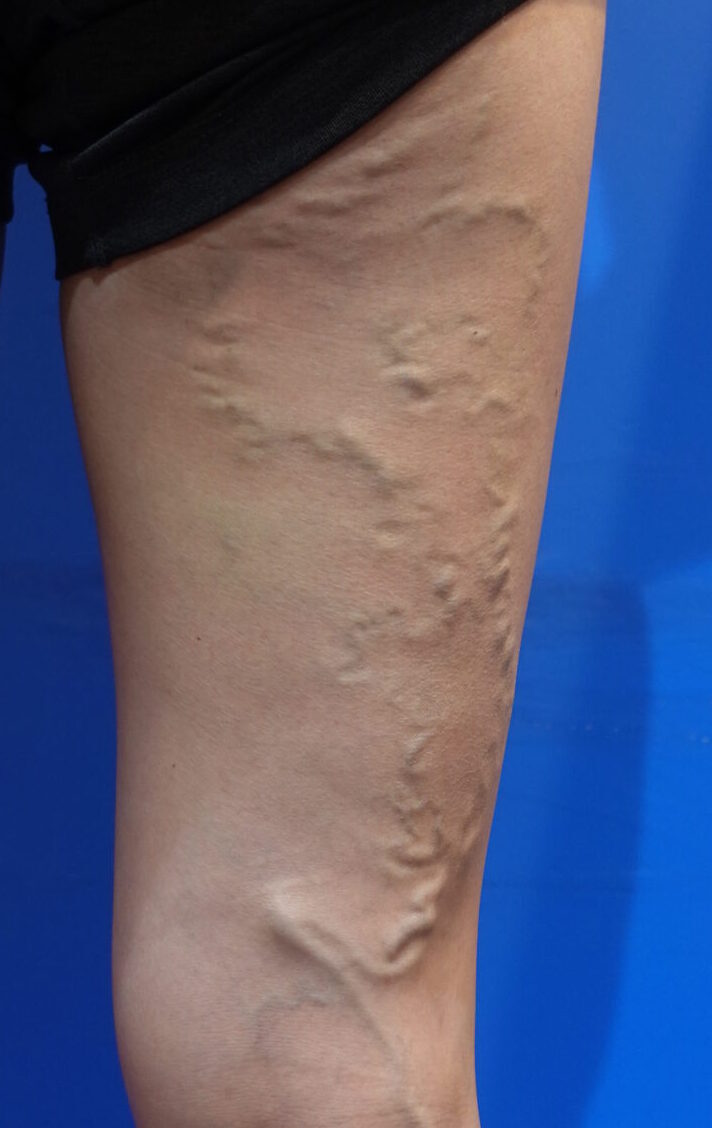
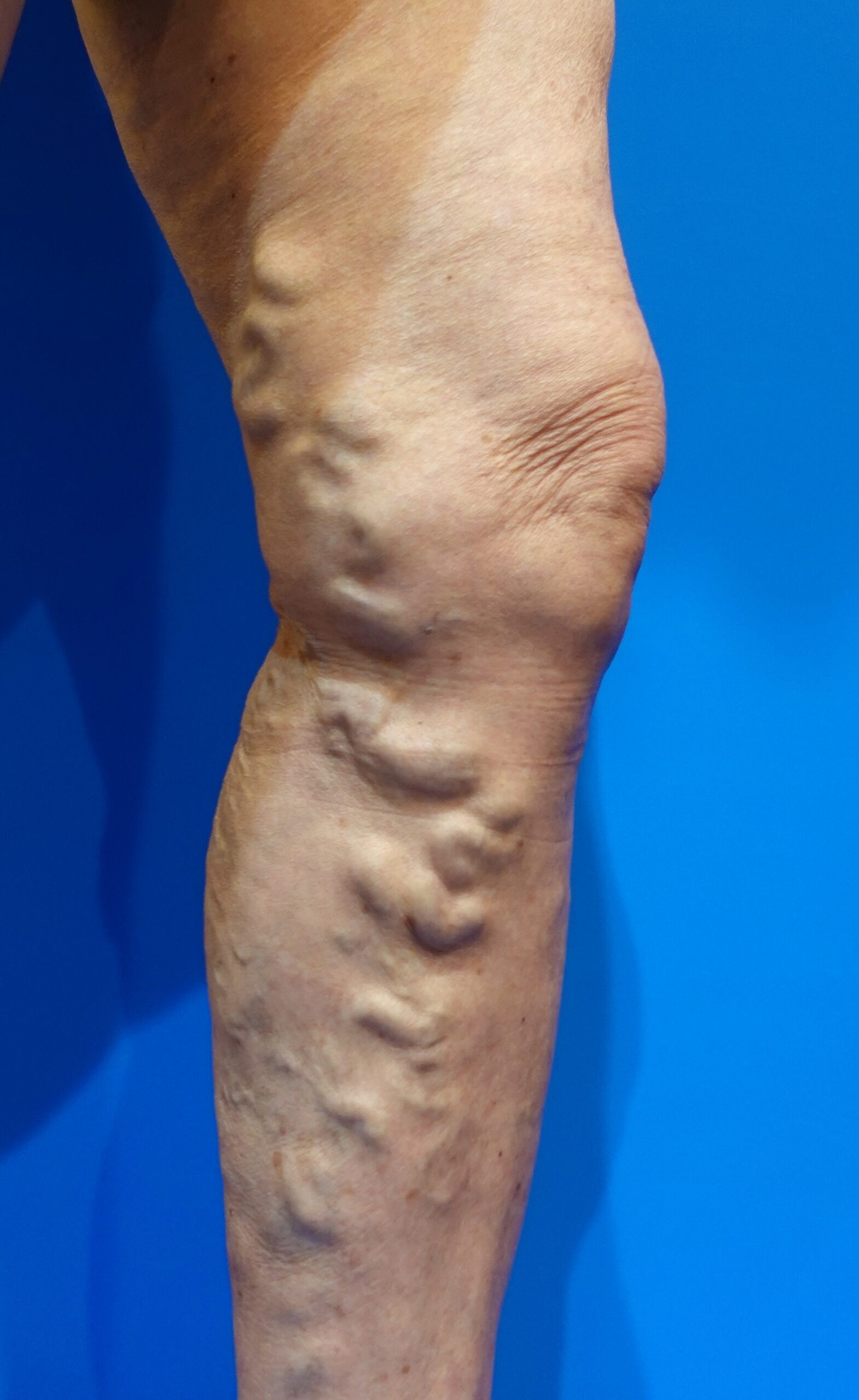
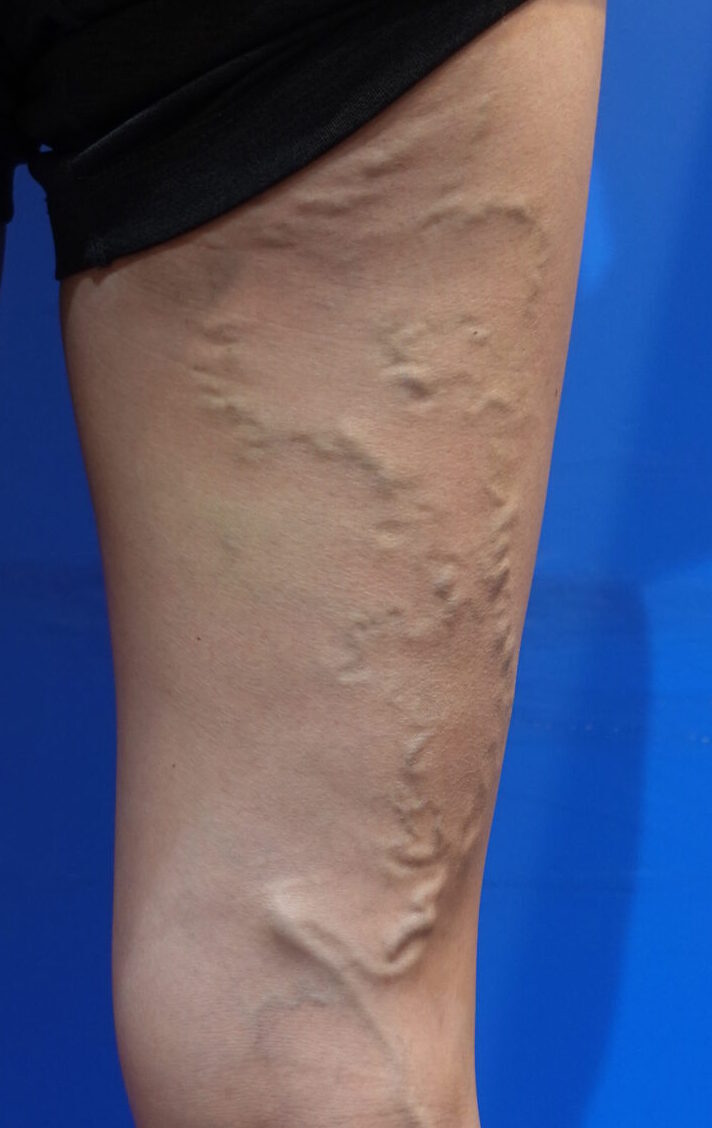
Vulvar varicose veins are a type of varicose vein that primarily occur in the vulva or the back of the thighs in women. This condition is often observed during or after pregnancy when the veins become enlarged and blood pools due to venous insufficiency. Vulvar varicose veins can cause not only aesthetic concerns but also discomfort and pain in the legs.
Causes of Vulvar Varicose Veins
While varicose veins in the legs occur in the superficial veins under the skin, vulvar varicose veins originate from the veins around the ovaries and uterus.
The primary cause of vulvar varicose veins is increased pressure within the veins. During pregnancy, the expanding uterus puts pressure on the pelvic veins, making varicose veins more likely to occur. Hormonal changes also play a role, softening the walls of the veins and making them more prone to dilation. Other contributing factors include genetic predisposition and prolonged standing or sitting.
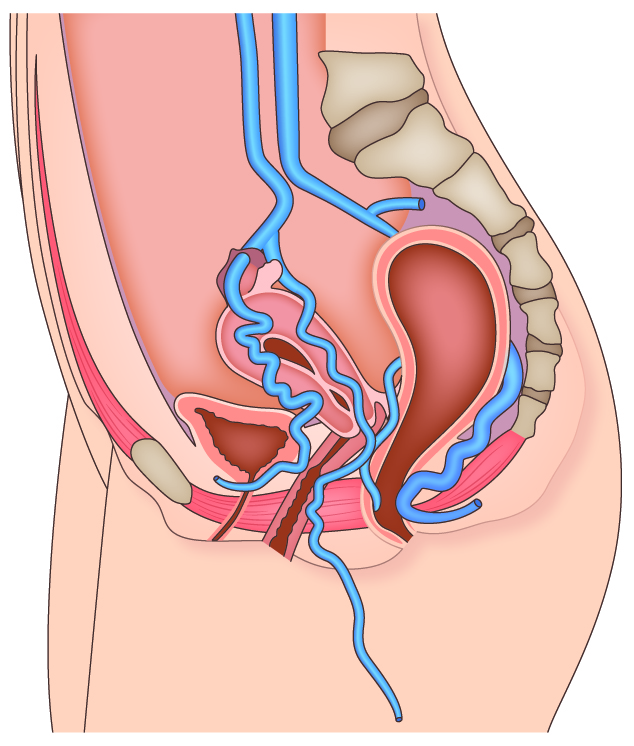
Symptoms of Vulvar Varicose Veins
・Swelling or bulging in the vulvar area
・Pain or discomfort
・A feeling of pressure or heaviness
・Twisted varicose veins in the vulva, buttocks, or back of the thighs
These symptoms tend to worsen during menstruation.
Diagnosis of Vulvar Varicose Veins
The diagnosis of vulvar varicose veins begins with a visual examination. An ultrasound (echo test) is then used to closely examine the veins, assessing blood flow and the presence of any reverse flow. For those experiencing pelvic pain, MRI or CT scans may be performed to check for dilation and reverse flow in the ovarian veins.
Treatment of Vulvar Varicose Veins
The treatment for vulvar varicose veins depends on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s preferences. For mild symptoms, the following measures are recommended:
– Wearing compression stockings
– Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting
– Taking regular breaks and elevating the legs
For severe symptoms that interfere with daily life, the following treatments are available:
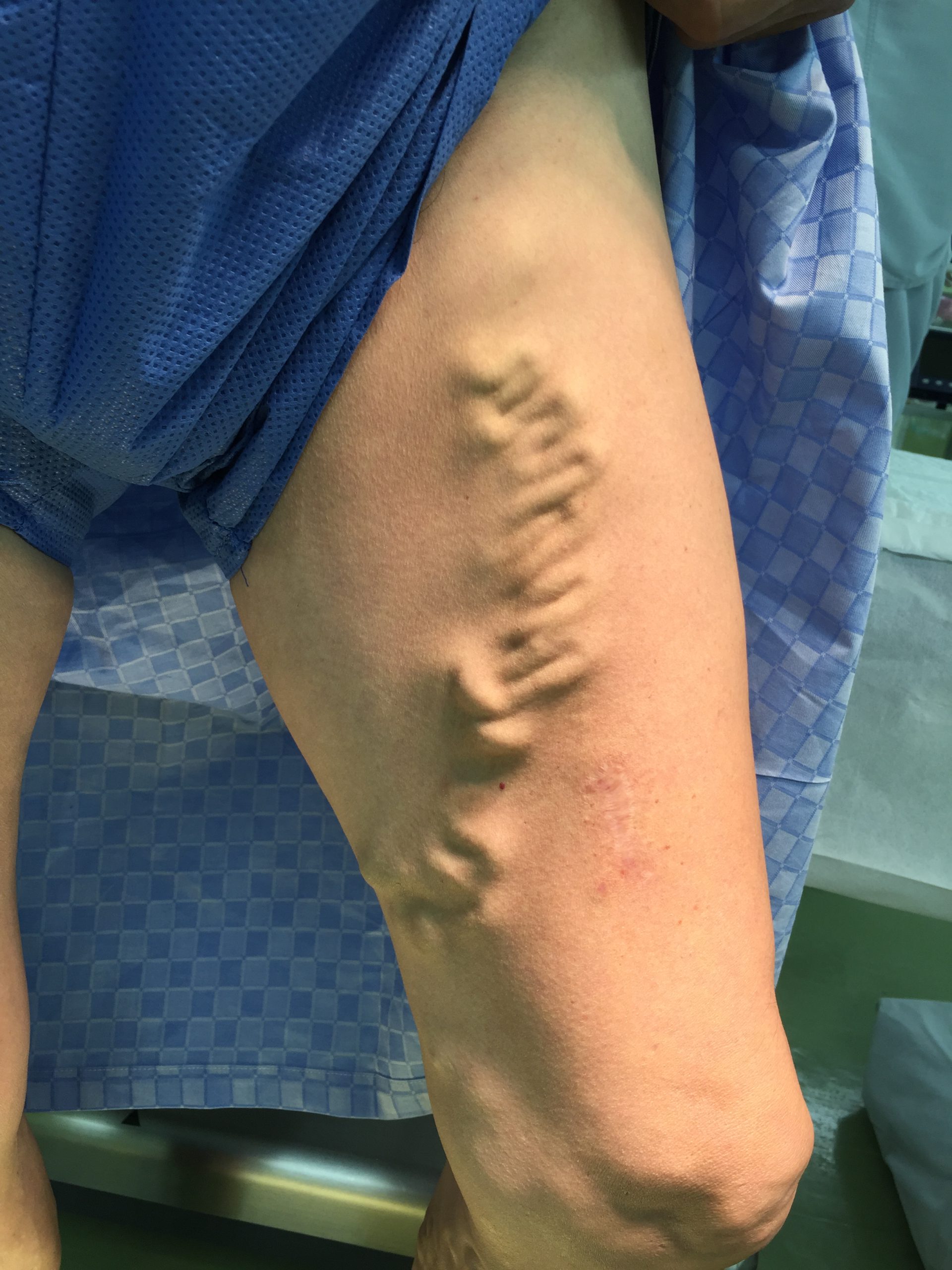
– Sclerotherapy : A treatment where a sclerosant is injected into the varicose veins to close them off.
– Endovenous Ablation: A treatment method where varicose veins are ablated and sealed using a laser catheter.
**Note: Sclerotherapy cannot be performed during pregnancy.**
If these treatments do not sufficiently alleviate symptoms, and there are varicose veins in the pelvis, additional treatments may be considered:
– Herbal Medicine: Taking a traditional Chinese medicine called Keishibukuryogan.
– Percutaneous Venous Embolization: A procedure in which a catheter is used to block the ovarian veins with metal coils or embolic agents to stop the reverse blood flow.
**Note: Percutaneous venous embolization cannot be performed during pregnancy.**
Prevention of Vulvar Varicose Veins
Preventive measures for vulvar varicose veins include:
– Regular exercise
– Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting
– Wearing compression stockings
– Managing weight
– Paying special attention during pregnancy and following medical advice.
Conclusion
Vulvar varicose veins are a condition that many women may experience, but with proper prevention and treatment, symptoms can be alleviated, and quality of life can be improved. If you suspect you have vulvar varicose veins, it is recommended to consult a specialist.