What Are Bleeding Varicose Veins? Risks During Bathing and How to Handle Them
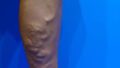
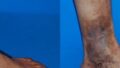
Bleeding varicose veins refer to a condition where varicose veins cause bleeding, commonly known as “blue blebs” in English. This condition is frequently seen in patients who have left their varicose veins untreated for many years, and bleeding can occur suddenly in daily life. Among these cases, bleeding during bathing is particularly common, requiring special caution.
Why Bleeding Often Occurs During Bathing
During a bath, the body warms up, causing blood vessels to dilate and blood flow to increase. As a result, venous pressure rises, making the already fragile veins more likely to rupture. For patients with bleeding varicose veins, the risk of vein rupture and bleeding is especially high during bathing. **This type of bleeding often erupts forcefully, causing significant alarm and fear in the patient.**
A Real-life Episode
In one case, a patient experienced sudden, profuse bleeding from their leg during a regular bath. Despite panicking and trying to stop the bleeding, they couldn’t manage to do so on their own, leading to their family calling an ambulance and rushing them to the hospital. This is not an isolated incident, but something that can happen as a consequence of leaving varicose veins untreated.
Once bleeding starts, it can be rapid, making it difficult for the patient to grasp the situation, which often leads to panic. If the blood loss is significant, there is a risk of going into shock due to the rapid depletion of blood. In such cases, it’s crucial to call an ambulance immediately and receive proper medical treatment at a hospital.
Causes of Bleeding Varicose Veins
Bleeding varicose veins occur due to the following factors:
1. Persistent elevation of venous pressure
When varicose veins prevent blood from properly returning to the heart, pressure builds up in the veins, causing them to expand and eventually rupture, leading to bleeding.
2. Thinning of the skin
The skin over the varicose veins becomes thin and prone to breaking, even with minor friction or trauma. Temperature changes during bathing can increase this risk.
3. Progression of untreated varicose veins
If left untreated for a long time, varicose veins deteriorate further, eventually leading to bleeding.
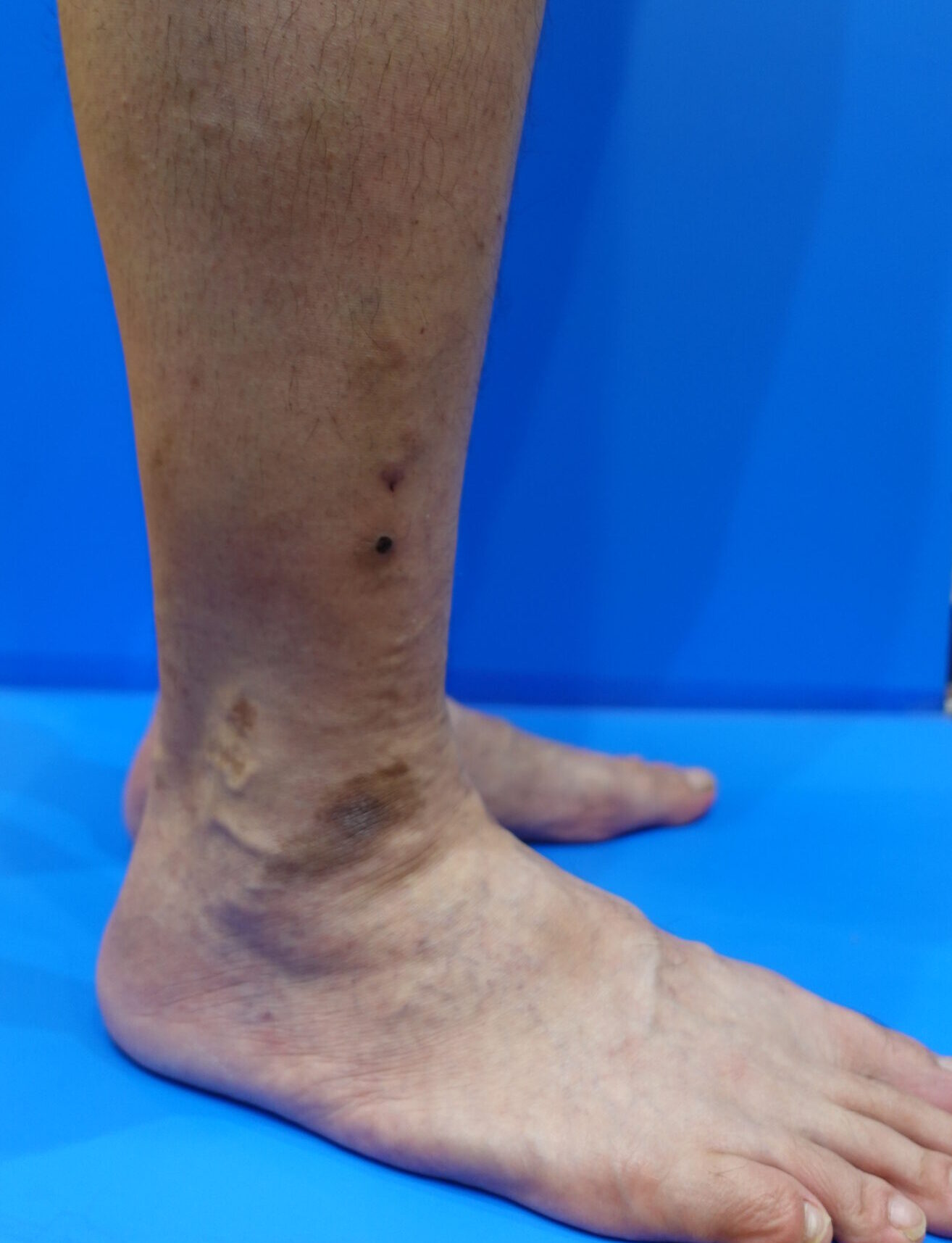
What to Do If Bleeding Occurs During Bathing
If a varicose vein ruptures and bleeding begins during a bath, it’s essential to take the following steps quickly:
1. Immediately apply pressure to the bleeding site
Use a clean towel or gauze to press firmly on the bleeding area to stop the flow of blood as the top priority.
2. Get out of the bath immediately
To stop the bleeding, get out of the bathtub right away and elevate your legs above heart level. This will slow the flow of blood and help reduce the bleeding.
3. Call an ambulance
If the bleeding does not stop, call an ambulance immediately. If there is significant blood loss, it’s difficult to stop the bleeding by yourself, so receiving treatment at a hospital as soon as possible is crucial.
Treatment for Bleeding Varicose Veins
The main treatments for bleeding varicose veins are as follows:
1. Sclerotherapy
A method where a drug is used to block the varicose vein and stop blood flow.
2. Endovenous ablation
A procedure where laser or radiofrequency catheters are used to cauterize the vein and block blood flow.
3. Endovenous embolization
A method that uses medical glue to close off the vein, blocking blood flow within the varicose vein.
Conclusion
Bleeding varicose veins pose a serious risk, especially during bathing when sudden bleeding can occur. To prevent such situations, early detection and proper treatment of varicose veins are essential. Additionally, adopting habits that reduce venous pressure, such as wearing compression stockings, can help lower the risk of bleeding in daily life. If you experience symptoms of blue blebs or varicose veins, consult a specialist early and take the necessary steps to manage the condition.